
Ask Indegene (Beta)
Hello, how can I help you today?
You may type your question or choose from the options below:
Thank you!
We'll be in touch. In the meantime, feel free to keep exploring!
Introduction
The global pharmaceutical industry is at a pivotal moment. As business models evolve, regulatory scrutiny intensifies, and the pace of innovation accelerates, pharma leaders face growing pressure to transform how their organizations operate. Generative AI (GenAI) is emerging as a game-changer, redefining the way content is created, workflows are orchestrated, and decisions are made.
For many years, Global Capability Centers (GCCs) have been pegged as the north star for achieving operational efficiency and scalability. But the foundational cost advantages of GCCs—centralization, scale, labor arbitrage—are rapidly eroding. Rising attrition, stagnant innovation, and high fixed costs are exposing cracks in the GCC model.
The solution is not incremental improvement. It's a strategic rethink. Functional Capability Centers (FCCs) offer a future-ready model that is domain-specific, agile, and GenAI-enabled. FCCs bring together specialized talent, modular AI agents, and flexible partner ecosystems to deliver high-value outcomes across Commercial, Medical Affairs, Clinical, Regulatory, and Pharmacovigilance functions.
This whitepaper explores why now is the time to pivot from traditional GCCs to GenAI-powered FCCs and how forward-looking pharma organizations can lead this transformation.
Understanding Global Capability Centers (GCCs)
GCCs are centralized, in-house hubs created by multinational enterprises to provide a broad spectrum of specialized support services. The services range from traditional enterprise functions, such as IT, finance, HR operations, and data analytics, to industry-specific capabilities like research and development (R&D), clinical operations, regulatory affairs, medical writing, pharmacovigilance, and commercial operations, that require domain knowledge and expertise.
Originally created to achieve cost efficiencies through labor arbitrage and process standardization, GCCs have evolved significantly over time. They are now seen as strategic assets playing a role at scaling global operations, influencing enterprise strategy, and enabling transformation – not just supporting it. However, as expectations evolve, cracks are beginning to surface.
The Erosion of the GCC Value Proposition
Despite the initial promise, most pharma GCCs today are struggling to deliver sustained strategic value, facing critical challenges that undermine their original objectives.

The Escalating Talent Retention Crisis
Talent retention is one of the most pressing challenges faced by GCCs today. A 2025 CIEL HR study reveals that 51% of GCCs in India identified talent retention as their biggest challenge.
The situation is aggravated by competition for talent driving up salary expectations. The concentration of GCCs in a few cities further intensifies the competition for a limited pool. For example, Bengaluru, in India, hosts numerous pharma GCCs including Teva, Alcon, Novo Nordisk, GSK and Merck. Employee costs in Indian GCCs have risen to 76.2% of total costs, up from 65.9% in 2020 and average employee salaries are projected to increase by 9.9% in 2025. The vicious cycle has started eroding the fundamental cost advantage of GCCs and hurting their profitability.
The rising cost base, coupled with the ongoing issues of talent retention and innovation stagnation raises concerns that the GCC model, especially when fully internalized, may shift from being a cost arbitrage play into a potential financial and agility liability.
The Emergence of Functional Capability Centers (FCCs)
Considering these challenges, a more dynamic and adaptive operational model is gaining traction: the Functional Capability Center (FCC).
An FCC is a specialized, domain-centric hub that centralizes domain-specific business functions that require specialized execution. Unlike traditional GCCs that aim for broader functional coverage, FCCs focus on building deep domain capabilities in high impact and often regulated business functions such as Commercial Operations, Medical Affairs, Regulatory Submissions, and Pharmacovigilance. FCCs can either be either managed completely inhouse or in a hybrid model that combines in-house leadership with external partnerships for execution. The hybrid FCC model leverages partner ecosystems for talent, technology, and operational agility, addressing the limitations of GCCs or in-house FCCs to achieve best-in-class talent on demand, improved retention, accelerated innovation, robust compliance, while also ensuring cost efficiency.
The goal of an FCC is to deliver expertise + agility + innovation + scalability minus the overheads of traditional GCCs.
GCC vs. FCC: What is the difference?
| GCC | In-house FCC | Hybrid FCC (with Partner) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope of Services | Best suited for enterprise-wide support functions such as IT, HR, finance, and data operations | Custom-built for specialized, domain-intensive functions like regulatory, medical, and commercial operations | Same as in-house FCC, with additional partner-enabled execution flexibility |
| Talent Model | Leverages generalist talent at scale, and is effective for stable, high-volume processes | Specialized talent hired and managed in-house to align with organizational culture and strategy | Combines in-house oversight with on-demand access to specialized talent via partner ecosystems |
| Scalability | Ideal for scaling steady-state functions with predictable resource needs and well-defined workflows | Designed for control, but less flexible. Challenging to scale rapidly for launches or market shifts | Highly adaptable—scales up/down based on dynamic business needs such as product launches or market expansion |
| Innovation Velocity | Dependent on internal investment and maturity; limited exposure to external innovation drivers | Same as GCC; innovation speed is tied to in-house capabilities and access to technology | Accelerates innovation through partners offering access to emerging technologies, pre-built AI agents, and domain-specific tools |
| Cost Efficiency | Offers cost advantages via labor arbitrage, but requires significant upfront investment (e.g., tech, real estate, hiring) | Same as GCC, with added cost of specialized in-house talent | Delivers cost efficiency through flexible resource models |
| Best Fit | Suitable for standardized, high-volume functions with consistent workload and centralized ownership, and standardized operations across regions | Ideal for regulated, domain-heavy functions where full control of talent, IP, and execution is critical | Best for complex, regulated functions requiring speed, specialization, and operational flexibility without compromising compliance |
How GenAI Elevates the FCC Model
The true potential of FCCs comes to life when powered by GenAI. GenAI-enabled FCCs can fundamentally how work gets done moving from manual execution to intelligent automation.
The scope of GenAI agents is no longer limited to traditional task bots. They can handle complex tasks like scientific summarization, content generation, and workflow orchestration. They don’t just execute; they learn, adapt, and optimize over time to maximize innovation and functional value. GenAI agents shift the role of human experts to judgment and oversight, bringing scale, speed, and real-time responsiveness to life sciences operations.
GenAI agents have the potential to automate 30-50% of high-value workflows across core pharma functions.

Here are some of the areas where GenAI can be applied to within the core pharma functions
Commercial Operations
- Content creation
- Omnichannel engagement and campaign operations
- Competitive intelligence
- Creative concepting and creative services
Medical Affairs
- Medical content creation
- Medical information & response
- Medical Legal Regulatory (MLR) Review
- Literature surveillance and review
- MSL field support and real-time engagement
- Scientific publication planning
- Advisory board insight summarization
- Congress coverage and summarization
Clinical Operations
- Protocol design and optimization
- Site selection and study feasibility
- Study build
- Clinical Data management
- Patient recruitment messaging
- Visit schedule optimization
- Risk-based monitoring plan generation
Regulatory Affairs
- Regulatory writing
- Regulatory intelligence and submissions
- Labeling updates and global variations tracking
- Change impact analysis for evolving regulations
- HA query response drafting
Pharmacovigilance
- Safety Signal Detection and Risk Management
- Adverse Event (AE) Intake, Triage, and Initial Narrative Generation
- Case Processing
- Aggregate report writing (PADER, PSUR, DSUR)
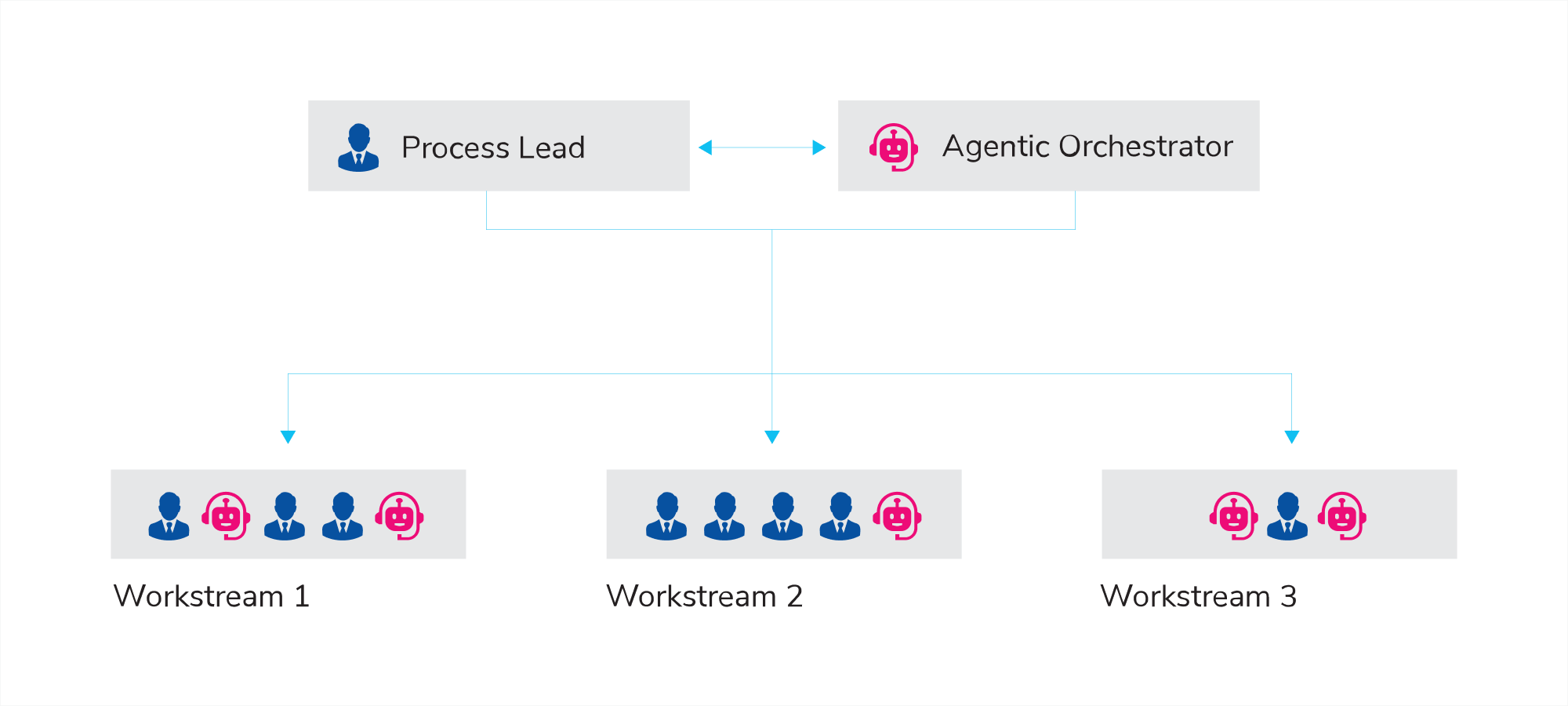
In GenAI-enabled FCCs, humans and agents collaborate to deliver business outcomes. FCCs evolve to include new roles like agent trainers, orchestration leads, and hybrid process designers, ensuring alignment between business goals and AI execution. Modular agent clusters further enable pharma enterprises to rapidly scale up or down in response to dynamically changing business requirements.
When powered by GenAI, FCCs evolve into adaptive intelligence hubs capable of delivering exponential value across pharma functions. With GenAI at the core of FCCs, traditional GCCs can quickly move from delivering cost efficiency to driving functional transformation, enabling pharma organizations to stay agile, innovative, and future-ready.
The GenAl-Enabled FCC Design Principles

Why Forward-Looking Pharma are Adopting the FCC Model
The move to GenAI-enabled FCCs is more than just an operational adjustment; it is a strategic necessity for the future of pharma. Over the past decade, Indegene has partnered with over 30 life sciences organizations, designing and managing their Global Delivery Centers (GDCs). Across these engagements, we have observed a consistent pattern: FCCs offer greater agility, depth, strategic value, and foster continuous innovation. The integration of GenAI further amplifies this value, accelerating the transformation agenda and unlocking next-level performance.
 Unlocking Value
Unlocking Value
By adopting the GenAI-enabled FCC model, pharma companies can shift their focus from operational execution to strategic impact. Pharma can channel their resources into high-value activities that drive competitive advantage, such as shaping market access strategies, advanced R&D insights, and navigating complex regulatory requirements. GenAI augments this by automating routine yet critical workflows, freeing up domain experts to focus on innovation, compliance and decision-making. A hybrid model takes it a step further by leveraging specialized partner ecosystems, allowing companies to scale and innovate faster without bearing the burden of internal buildout. It reduces the operational overhead of managing multiple functions under a single GCC umbrella and enables targeted resource allocation investing where value is highest, while outsourcing execution to trusted, AI-augmented partners. Together, these models unlock smarter, leaner, and more strategic operations helping pharma organizations maximize ROI while accelerating time-to-impact across core functions.
 Hyper-Specialization
Hyper-Specialization
FCCs, both in-house and hybrid, enable pharma organizations to tailor processes and attract talent specifically suited to the unique demands of specific functions—whether addressing the rigorous compliance requirements within regulatory affairs or the scientific knowledge needed to develop medical content or creative needs in marketing content development. With hyper-specialization, companies can deliver higher quality outputs, reduce errors, and achieve higher operational efficiencies.
 Increased Appetite for Innovation
Increased Appetite for Innovation
The advantage of hybrid FCCs is particularly evident in the context of GenAI. Incorporating GenAI capabilities within a traditional GCC/in-house FCC setup can require extensive overhauls, retraining initiatives, change management processes, and the technical expertise to develop agents and integrate them into cohesive agentic workflows. On the other hand, hybrid FCCs allow organizations to leverage specialized partner networks that provide plug-and-play agentic workflows, pre-trained professionals, established frameworks, and dependable governance models, facilitating a smooth and compliant integration of GenAI into core pharma workflows.
 Higher Cost Efficiency
Higher Cost Efficiency
While GCCs/in-house FCCs may promise savings through labor arbitrage, they frequently come with hidden expenses related to recruitment, turnover backfills, salary adjustments, governance structures, and lengthy ramp-up times. In contrast, hybrid FCCs avoid the hidden costs of full-scale GCCs by concentrating investment where it matters and using external vendors for execution agility and cost control.
 Flexibility to Scale
Flexibility to Scale
Hybrid FCCs provide pharmaceutical companies with the flexibility to scale up or down in alignment with fluctuating project demands. Whether it’s a product launch, pharmacovigilance alert, or a critical regulatory filing, pharma organizations can rapidly deploy expert teams through pre-vetted vendor ecosystems—accelerating execution. Unlike traditional GCCs/in-house FCCs, which have set teams and structures, FCCs enable quick access to skilled professionals, enabling enterprises to scale resources up or down with fluctuating business demands. This setup helps overcome talent scarcity and rising attrition, as well as reduce hiring time and salary costs.
GenAI further amplifies this agility. Modular GenAI agents can be rapidly configured and deployed, and can take on tasks such as content generation, triage, and data summarization in real time, allowing pharma teams to flex not just people but also digital capacity. This dual-scalability—human and AI—makes hybrid FCCs the ideal model for dynamic, high-impact pharmaceutical operations.
 Lower Risk, Higher Maturity
Lower Risk, Higher Maturity
FCCs offer tighter compliance, stronger functional governance, and faster maturity curves — which are critical for regulated pharma functions.
Fundamentally, FCCs shift the focus from infrastructure to outcomes. They are more than just an alternative to GCCs; they represent an evolution in operational strategy. This hybrid model brings in strategic agility, promotes innovation, and accelerates transformation in functions that have traditionally encountered inadequate support from established operational frameworks.
Conclusion
GenAI-Enabled FCCs: The Future of Intelligent Pharma Operations
The future of pharmaceutical operati ons is going to be specialized, intelligent, and driven by AI. As pharma leaders confront rising complexity, cost pressures, as well as innovation and ROI mandates, the legacy GCC model is no longer delivering the effectiveness it once promised. While GCCs remain effective for enterprise-wide support functions like IT, HR, finance, and data operations, FCCs offer a smarter, purpose-built approach for specialized functions, designed to align closely with their business needs.
The transformational impact of Generative AI makes this shift even more compelling. GenAI agents empower functional teams, by handling complex tasks and freeing up experts to focus on critical strategic thinking, innovation, and complex decision-making. It brings unmatched speed and capacity to pharma operations. Hybrid GenAI-powered FCCs take it one notch higher as they provide the flexibility to scale quickly, access cutting-edge technology, and integrate innovation without heavy internal investments.
Pharma leaders who embrace purpose-built hybrid FCCs powered by Generative AI can shift from infrastructure-heavy support to a nimble, innovation-driven model that accelerates breakthroughs, improves patient outcomes, and positions their organizations to thrive in the next era of healthcare.
References
Let's Partner to Commercialize with Confidence

